The bike hub is the primary element that affects the speed, stability, and overall performance of your ride. Whether you’re a road cyclist aiming for efficiency, a mountain biker navigating tough trails, or a BMX rider perfecting your tricks, the right hub can make a noticeable difference. Selecting the best hub affects handling, longevity, power transmission, and smooth riding, so it’s not only for mechanics.
A bike hub connects many crucial components that contribute to your bike’s functionality. Understanding what is a bike hub and the different types of hubs and knowing how to select and maintain them properly is essential for any cyclist. With a bit of guidance on selection, maintenance, and hub essentials, you’ll enjoy a better riding experience with enhanced efficiency and longer-lasting performance on every ride.
What Is a Bike Hub?
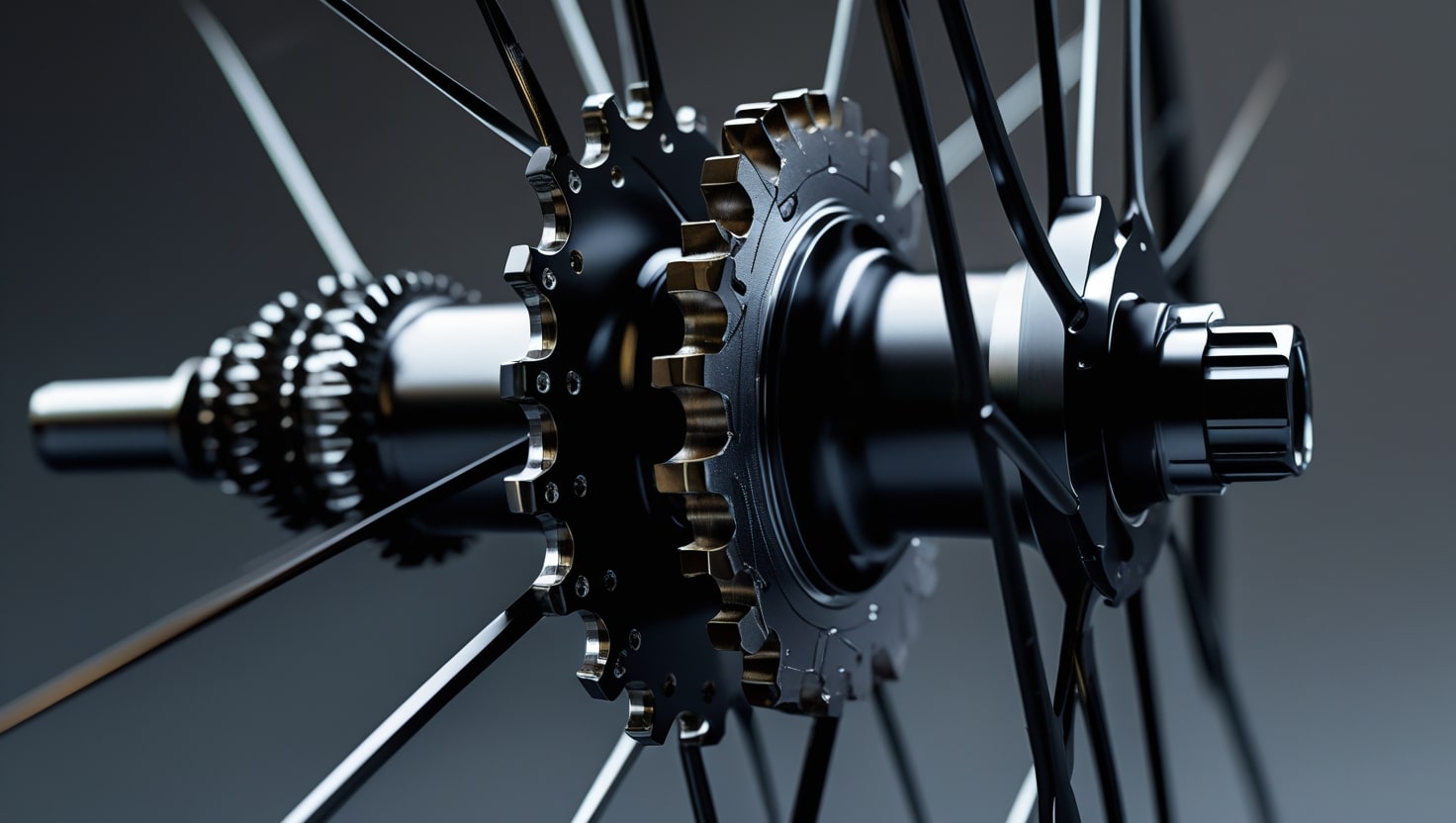
The bike hub is a key part of the wheel, connecting the spokes to the axle and ensuring the smooth rotation of the wheel. It affects speed, control, and efficiency, making it a vital component of the bike’s performance. The freehub mechanism, which controls the power transfer from the pedals to the wheel, and bearings that lower friction are located inside the hub. This makes the hub an essential component for a smooth and efficient ride.

Front Hub
The front hub is a vital component of your bike, consisting of a spindle that’s attached to the rim of the wheel. It has bearings that make the wheel spin smoothly, guaranteeing a comfortable ride. The component that secures the front wheel to the bicycle is the fork, to which the hub’s axle is attached.
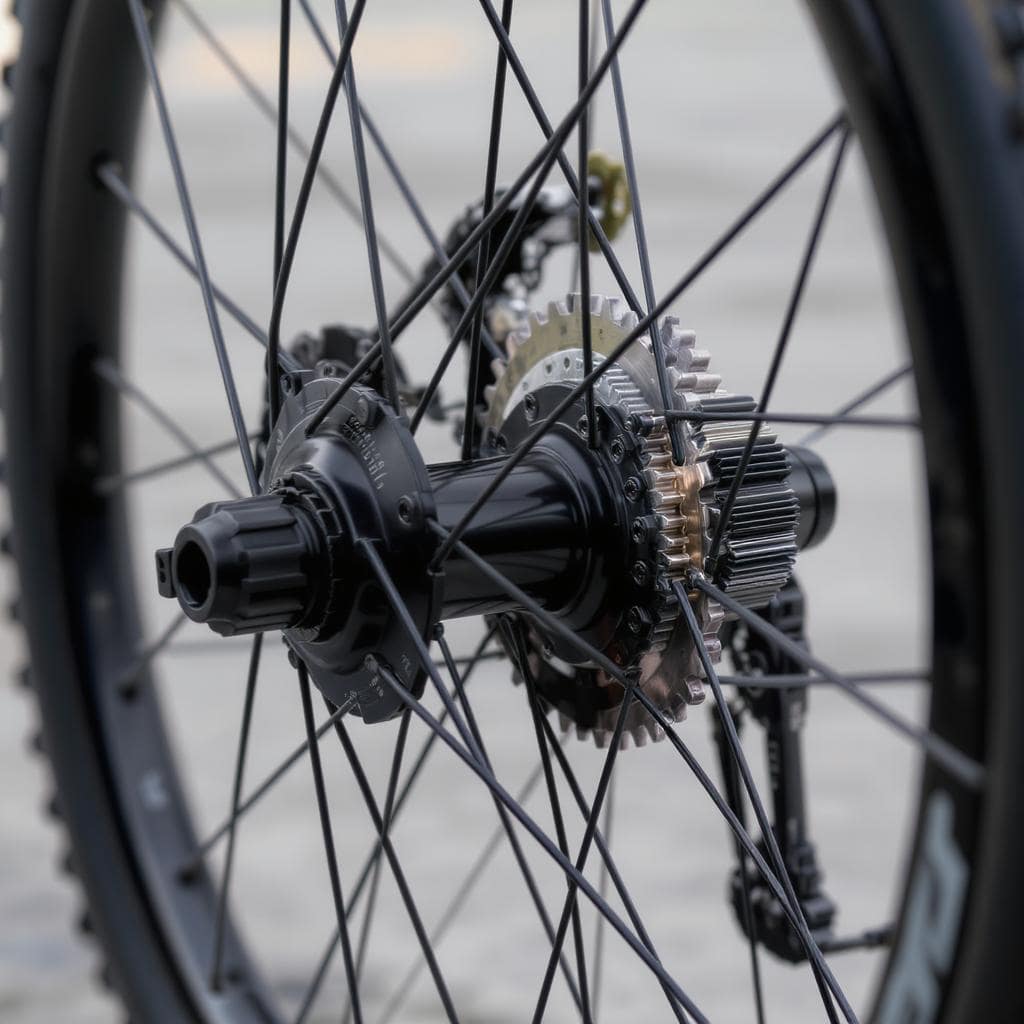
Rear Hub
Compared to the front hub, the rear hub is more intricate and has extra parts made to fit the bicycle’s gears. Additionally, it has a freewheel mechanism that lets the rider pedal backwards without using the rear wheel or chain. This makes the rear hub especially useful when the rider needs to coast or brake, offering better control and a smoother riding experience.
Internal Structure of a Bike Hub
The hub consists of several components that work together to ensure proper function.
The axle joins the hub to the bike’s frame or fork.
In order to reduce friction and enable smooth rotation, bearings are essential.
Bearings come in two types: sealed (requiring low maintenance) and loose ball (which is adjustable but needs more upkeep).
The freehub mechanism is found in rear hubs only and controls the drivetrain, engaging and disengaging as needed.
How Freehub Mechanisms Affect Performance
The ride might be affected by freehub variations depending on the engagement angle and ratchet count.
A higher ratchet count (more teeth) results in quicker engagement, boosting pedaling efficiency.
While wider angles may delay engagement but offer smoother coasting, smaller angles facilitate faster power transmission.
The sound differences in engagement points often lead to louder clicks, which many riders find useful as an audible indicator of their bike’s performance.

Types of Bicycle Hubs
Bike hubs are designed to meet the unique needs of different cycling styles. Each variant differs in design, strength, and performance features to enhance the overall riding experience.
1. Road Bike Hubs
Road bike hubs are ideal for long rides or races because of their lightweight construction and low rolling resistance. These hubs are designed to maximize speed and aerodynamics through seamless, effective power transfer. They prioritize performance and are perfect for racing and long-distance cycling. Many road bike hubs feature a quick release (QR) axle, making it easier to remove and install a wheel.
Road bike hub bearings are usually high-precision, made to minimize friction, increase efficiency, and need less upkeep.
2. Mountain Bike Hubs
In order to endure the difficulties of rocky terrain, jumps, and unexpected impacts, mountain bike hubs are designed for strength and high load capacity. These hubs’ sealed bearings help shield them from water, mud, and grime, lowering maintenance costs and guaranteeing enduring performance. Their design makes them ideal for challenging conditions, ensuring you can rely on them for stopping power with disc brakes, which are commonly brake-compatible in mountain biking.
In place of the more common quick-release methods, many mountain bike hubs use thru-axles, which increase rigidity and improve handling on rocky terrain. The combination of these features ensures a smooth, reliable ride, even in the toughest environments, with fewer maintenance requirements and better overall control.
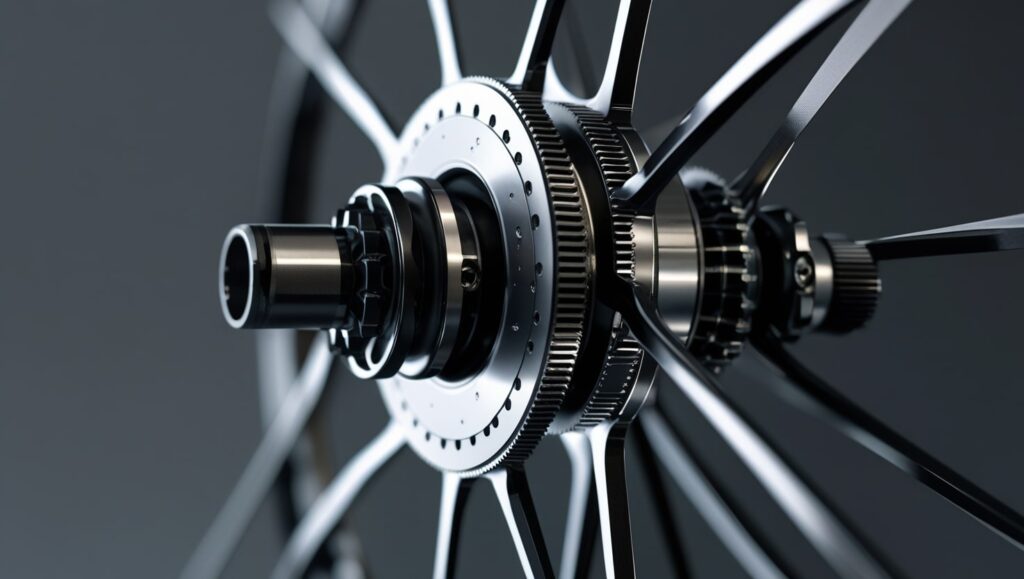

3. Track Bike Hubs
Track bike hubs are designed with a minimalist approach, focusing on high-speed performance and velodrome racing. For riders who require exact control over their speed, these hubs are perfect because they are designed to offer maximum efficiency and lowest resistance. A fixed-gear connection between the powertrain and the rear wheel is ensured by the fact that track bike hubs, in contrast to other hubs, lack a freewheel mechanism, so the rear hub is constantly engaged with the pedals.
This design allows for backpedaling to control braking, offering a direct and reliable way to manage speed without the need for separate braking systems.
4. BMX Hubs
BMX hubs are ideal for aggressive riding styles like street, park, and dirt jumping since they are designed to promote strength and impact resistance. These hubs are designed to endure heavy landings, grinding, and rapid torque changes that come with intense riding. They frequently have strong axles and large bearings to guarantee durability.
Depending on the rider’s inclination, some BMX hubs use coaster brakes, while others have cassette-style mechanics.
5. Trick Hubs (Freestyle Hubs)
One of the most notable features of some freestyle hubs is the freecoaster hub, which allows the rear wheel to rotate backward without engaging the pedals. This feature is ideal for performing smooth pedal backspins and fakie tricks, giving freestyle riders better control over their movements. Trick hubs are rear hubs specifically designed for modern BMX tricks and street riding. These hubs typically have an internal ratchet mechanism that makes it easy for riders to perform complex maneuvers.
Freestyle hubs are crucial for anyone wishing to advance their riding since they provide riders more creative control and improve their ability to execute a range of feats and tricks in the park or on the street.
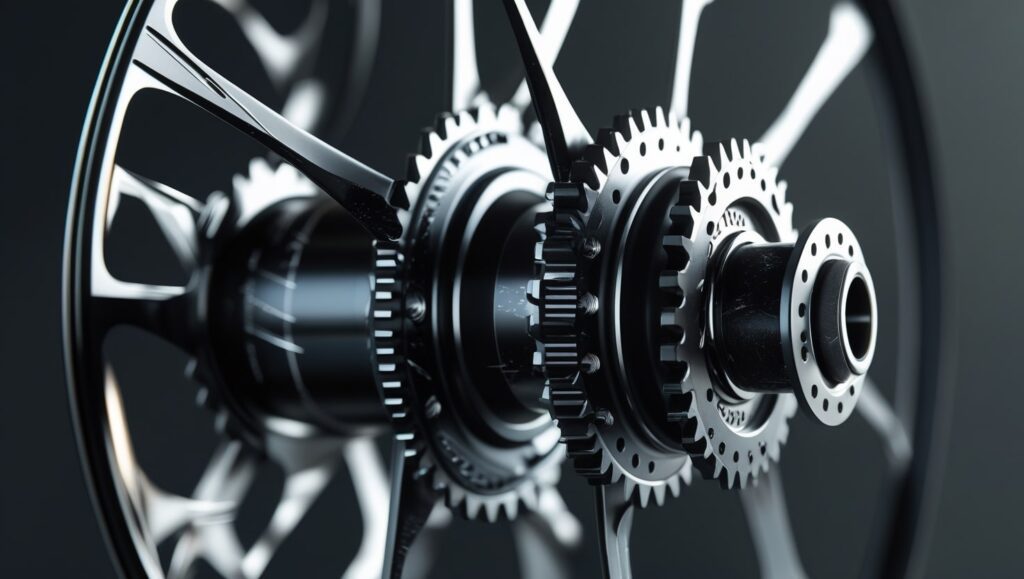
Function of Bicycle Hubs
Support the Wheel: Bicycle hubs enable smooth wheel rotation by bearing the weight of the rider and the bicycle.
Minimize Friction: Hubs are designed to minimize friction, reducing the bike’s efficiency. Grease or oil is used to lubricate the hub’s internal bearings, ensuring smooth rotation and less friction.
Transfer Power: The hubs transfer power from the rider’s legs to the wheel, helping the bike move forward.
Gear Accommodation: Rear hubs are designed to hold gears, which enable riders to go quicker on flat terrain or climb hills.
How to Choose the Right Bike Hub
1. Bike Type:
Choosing the right bike hub starts with understanding your bike type. Different bikes require different hub designs. For road bikes, hubs focus on lightweight efficiency, while mountain bikes emphasize durability and off-road performance. If you’re into track riding, you’ll need fixed-gear hubs, and for those riding BMX, the hubs are built for impact resistance. Ensure your hub is designed specifically for your riding style to maximize performance.
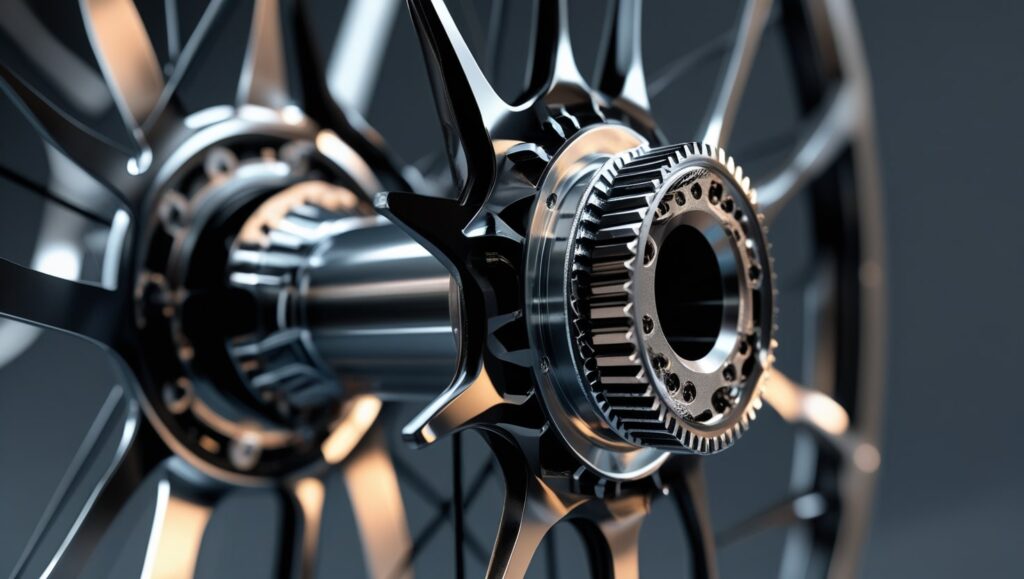
2. Frame and Fork Spacing:
When selecting a hub, frame and fork spacing plays a crucial role. Bike hubs come in various widths, so it’s essential to measure the spacing correctly. For example, mountain bikes typically have 110mm front and 148mm rear widths, whereas road cycles typically have 100mm front and 130mm rear widths. Make sure you match the hub’s width to the frame and fork for a perfect fit.
3. Brake Type:
Either disc brakes or rim brakes can be installed on hubs. If your bike has disc brakes, make sure to choose a hub that is compatible with the correct mounting system—whether it’s six-bolt or Center Lock. The brake type determines how the hub interfaces with your braking system, so it’s important to pick the right one for safe and efficient braking.
4. Bearing Type:
Bearings are another key factor when selecting a hub. Sealed bearings require less maintenance and provide better protection against dirt and moisture, keeping your hub running smoothly for longer. On the other hand, loose ball bearings are easier to service but need more frequent cleaning and adjustment.
5. Hub Compatibility:
Lastly, hub compatibility is essential for a proper fit. Quick-release (QR) hubs are common on road bikes, but if you ride mountain or gravel bikes, you might prefer thru-axles for better stiffness and security. Always ensure the hub you choose matches your axle system for the best performance.
Bike Hub Maintenance Guide
1. Routine Cleaning:
Remove the wheel to easily access the hub for cleaning.
Wipe off dust and dirt using a dry cloth or brush, which helps prevent debris buildup that could affect performance.
Avoid using high-pressure water as it can force moisture into the hub, leading to rust or bearing damage.
2. Inspect the Hub Axle and Bearings:
Shake the wheel gently to check for loose hub axles.
The axle or bearings may need to be adjusted or replaced if there is excessive play.
Listen for any unusual noises like grinding or rough spinning, as these may indicate worn bearings that require servicing.

3. Lubrication and Maintenance:
Disassemble the axle and bearings using cone wrenches if necessary.
To get rid of old grease and dirt, use degreaser or alcohol to clean the bearings and internal parts.
Apply high-quality bearing grease to reduce friction and prevent premature wear of the bearings.
Related: Convert Mountain Bike To Electric
4. Avoid Over-Tightening:
Axle nuts should be properly adjusted to maintain smooth rotation.
If the nuts are too loose, the hub may feel unstable and wobble.
If too tight, the added pressure can damage the bearings, causing resistance in the hub.
5. Environmental Protection:
After riding in damp, muddy, or dusty circumstances, clean the hubs right after to avoid pollutants harming the internal parts.
Use waterproofing measures like sealed waterproof rings to protect against moisture infiltration, especially in harsh riding conditions.
6. Regular Inspections:
To guarantee peak performance, do a complete hub service every six months or after 5,000 kilometers of riding.
Mountain and off-road riders should inspect and service their hubs more often due to increased exposure to dirt, water, and impact forces.
Conclusion
When it comes to a bicycle hub, it’s a crucial component that plays a significant role in ensuring a smooth and efficient ride. Having a good hub that can sustain your weight and lower friction is crucial, regardless of whether you’re a professional or recreational cyclist. If you’re looking to purchase a new bicycle or upgrade an existing one, be sure to invest in a hub that meets your specific needs and budget for the best overall experience.
Related: 12 Best Mid Drive eBike








